Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin block reward will decrease from 6.25 to 3.125 coins in approximately
Estimated date & time of reward drop:
18 April 2028 02:54
* Bitcoin data powered by
blockchair
#843,606
Current Block
#1,050,000
Bitcoin Halving at Block
#206,394
Block To Go
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin
has a total supply of 21 million. The underlying code ensures that only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist. Bitcoin’s finite supply is a strong economic statement and supports its value system.
Bitcoin is distributed through mining. The 21 million bitcoins in existence are scheduled to be mined through the year 2140. That is, the last bitcoin is expected to be mined in the year 2140. At the current rate of emission, the unmined bitcoin will be exhausted before this speculated time. Almost 90% of bitcoin’s total supply has been mined. About 900 bitcoins are mined per day, currently.
To sustain the emission and increase scarcity, the number of bitcoin emitted per block is regularly reduced. This process of reducing the bitcoin emission per block is known as Bitcoin Halving.
After a predetermined block height (a number that is used to indicate a particular block), the amount of bitcoin emitted per block is reduced to half of the previous number. For bitcoin new halving occurs after an interval of 210,000 blocks or 4 years.
The most recent (2020) halving reduced bitcoin emission from 12.5 bitcoin per block to 6.25 bitcoin per block. This means that instead of 12.5 bitcoins, miners will now be rewarded with 6.25 bitcoins per block mined.
Bitcoin is distributed through mining. The 21 million bitcoins in existence are scheduled to be mined through the year 2140. That is, the last bitcoin is expected to be mined in the year 2140. At the current rate of emission, the unmined bitcoin will be exhausted before this speculated time. Almost 90% of bitcoin’s total supply has been mined. About 900 bitcoins are mined per day, currently.
To sustain the emission and increase scarcity, the number of bitcoin emitted per block is regularly reduced. This process of reducing the bitcoin emission per block is known as Bitcoin Halving.
After a predetermined block height (a number that is used to indicate a particular block), the amount of bitcoin emitted per block is reduced to half of the previous number. For bitcoin new halving occurs after an interval of 210,000 blocks or 4 years.
The most recent (2020) halving reduced bitcoin emission from 12.5 bitcoin per block to 6.25 bitcoin per block. This means that instead of 12.5 bitcoins, miners will now be rewarded with 6.25 bitcoins per block mined.
Why Is Bitcoin Halving Important?
Bitcoin halving serves both economic and sustenance purposes.
On the aspect of bitcoin’s economy, halving creates a scarcity pattern for bitcoin. Against a varying demand, bitcoin halving reduces the rate at which bitcoin is supplied. The demand for bitcoin has seen a consistent rise over the years, this has been met by a constant decrease in the supply rate.
To say the least, it solidifies bitcoin’s status as a store of value. A slower supply against a rising demand ensures that bitcoin is worth even more over time. Considering market sentiments and the craving for scarce commodities, the effect of Halving on bitcoin’s value exceeds the boundaries of demand and supply economics.
An estimated 3 million bitcoins are currently lost to forgotten wallet details, lost hard drives, and bitcoins owned by deceased investors. The majority of this figure is lost without chances of recovery. Considering the rate at which bitcoin is completely lost, bitcoin is a deflationary currency, and halving further complements this scarcity.
On the aspect of sustenance, bitcoin mining incentivizes miners to validate blocks and guard the bitcoin network. Miners ensure that the blockchain is protected from malicious attempts. As long as bitcoin’s emission continues, miners are drawn to the mining exercise and the bitcoin blockchain remains secured.
Halving sustains supply and hence mining. With halving creating scarcity, driving up value, and slowing down the emission rate of bitcoin, more miners are attracted to secure the blockchain for a longer period of time.
On the aspect of bitcoin’s economy, halving creates a scarcity pattern for bitcoin. Against a varying demand, bitcoin halving reduces the rate at which bitcoin is supplied. The demand for bitcoin has seen a consistent rise over the years, this has been met by a constant decrease in the supply rate.
To say the least, it solidifies bitcoin’s status as a store of value. A slower supply against a rising demand ensures that bitcoin is worth even more over time. Considering market sentiments and the craving for scarce commodities, the effect of Halving on bitcoin’s value exceeds the boundaries of demand and supply economics.
An estimated 3 million bitcoins are currently lost to forgotten wallet details, lost hard drives, and bitcoins owned by deceased investors. The majority of this figure is lost without chances of recovery. Considering the rate at which bitcoin is completely lost, bitcoin is a deflationary currency, and halving further complements this scarcity.
On the aspect of sustenance, bitcoin mining incentivizes miners to validate blocks and guard the bitcoin network. Miners ensure that the blockchain is protected from malicious attempts. As long as bitcoin’s emission continues, miners are drawn to the mining exercise and the bitcoin blockchain remains secured.
Halving sustains supply and hence mining. With halving creating scarcity, driving up value, and slowing down the emission rate of bitcoin, more miners are attracted to secure the blockchain for a longer period of time.
Bitcoin Halving Chart
The chart below illustrates the developments in tokenomics and miners’ rewards as a result of bitcoin halving. It shows a consistent decrease in block rewards as the supply gradually slows down with each halving.
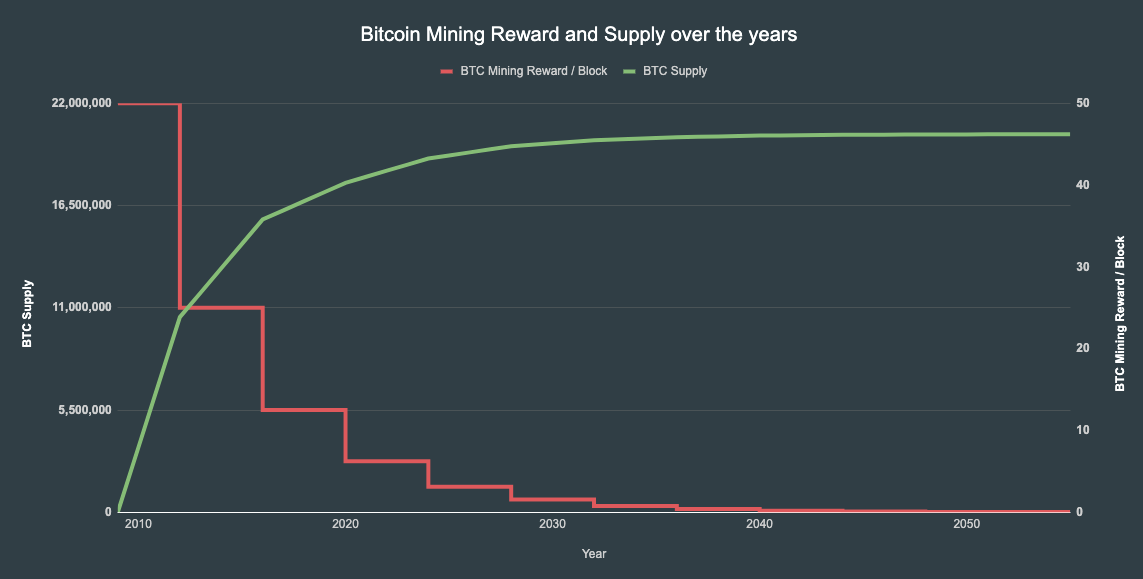
Bitcoin Halving Dates
The halving algorithm was developed in the initial bitcoin release. Bitcoin’s white paper featured an explanation for a constant reduction in emissions and the schedule for this event.
Four years after bitcoin’s genesis block and after over 10 million bitcoins and 210,000 blocks have been mined, the first halving occurred on November 28, 2012. The first halving event reduced the bitcoin mining reward to 25 bitcoins per block from an initial 50 bitcoins per block.
The recent halving occurred in April 20, 2024 at the block height of 840000, reducing the bitcoin block reward from 6.25 to 3.125 bitcoin.
Four years after bitcoin’s genesis block and after over 10 million bitcoins and 210,000 blocks have been mined, the first halving occurred on November 28, 2012. The first halving event reduced the bitcoin mining reward to 25 bitcoins per block from an initial 50 bitcoins per block.
The recent halving occurred in April 20, 2024 at the block height of 840000, reducing the bitcoin block reward from 6.25 to 3.125 bitcoin.
When Is The Next Bitcoin Halving?
The next bitcoin halving is expected to happen on April 17, 2028, at the block height of 1050000. When this happens, bitcoin’s block reward will be reduced to 1.5625.
When Was The Last Bitcoin Halving?
The last bitcoin halving happened on April 20, 2024, at the block height of 840000. Bitcoin’s block reward was reduced from 6.25 to 3.125.
Here’s a table of Bitcoin Halving Dates
| Halving count | Date | Block height at halving | Block reward before halving(bitcoin per block) | Block reward after halving(bitcoin per block) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2012-11-27 | 210,000 | 50 | 25 |
| 2 | 2016-07-09 | 420,000 | 25 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 2020-05-11 | 630,000 | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| 4 | 2024-04-20 | 840,000 | 6.25 | 3.125 |
| 5 | 2028-04-17 | 1,050,000 | 3.125 | 1.5625 |
| 6 | 2032 | 1,260,000 | 1.5625 | 0.78125 |
| 7 | 2036 | 1,470,000 | 0.78125 | 0.396025 |
How Does Bitcoin Halving Affect The Price of Bitcoin?
Halving is a double-edged sword, for different groups, it means different things.
For investors, halving means a reduction in the frequency at which new bitcoins are generated and less propensity for miners to sell. Historical data indicates a positive effect of the expected scarcity on the investors’ psychology. Investors expect a rise in the value of bitcoin and more buys could follow.
Past mining events have seen positive effects, however, the effect of halving events on bitcoin price is prone to variations, depending on prevailing market conditions.
Building up to the 2020 halving, bitcoin’s price rose about 40% thanks to investor behavior and the speculations that followed the event. Sequel to the halving, bitcoin’s value rose to three times its previous All-time-high, hitting a new high of $67,000.
For miners, halving ultimately means a reduced reward. Setting up and maintaining a bitcoin mining facility is a costly venture and miners expect the block rewards to at least offset these expenses.
When the reward is halved, miners’ revenue reduces by half. Considering the presiding values and cost of running a bitcoin mine, many miners might shut down their mining set-up if they are unable to maintain the facility with the calculated post-mining revenue.
As miners halt their activities, the mining hashrate is expected to drop. A decrease in mining hashrate could slow the bitcoin network and cause transactions on the blockchain to be executed later than they used to. Hashrate could return to former values if bitcoin’s price continues to rise and miners see profitability in running a mine again.
For investors, halving means a reduction in the frequency at which new bitcoins are generated and less propensity for miners to sell. Historical data indicates a positive effect of the expected scarcity on the investors’ psychology. Investors expect a rise in the value of bitcoin and more buys could follow.
Past mining events have seen positive effects, however, the effect of halving events on bitcoin price is prone to variations, depending on prevailing market conditions.
Building up to the 2020 halving, bitcoin’s price rose about 40% thanks to investor behavior and the speculations that followed the event. Sequel to the halving, bitcoin’s value rose to three times its previous All-time-high, hitting a new high of $67,000.
For miners, halving ultimately means a reduced reward. Setting up and maintaining a bitcoin mining facility is a costly venture and miners expect the block rewards to at least offset these expenses.
When the reward is halved, miners’ revenue reduces by half. Considering the presiding values and cost of running a bitcoin mine, many miners might shut down their mining set-up if they are unable to maintain the facility with the calculated post-mining revenue.
As miners halt their activities, the mining hashrate is expected to drop. A decrease in mining hashrate could slow the bitcoin network and cause transactions on the blockchain to be executed later than they used to. Hashrate could return to former values if bitcoin’s price continues to rise and miners see profitability in running a mine again.
What Happens When All Bitcoins Are Mined?
You’ll certainly wonder how miners on the bitcoin network will be compensated for guarding the bitcoin blockchain when the bitcoin supply has been completely mined in the year 2140. When all bitcoins are mined, miners’ incentivization will be sustained by transaction fees paid by users of the bitcoin blockchain.


 Or check it out in the app stores
Or check it out in the app stores

